One of the problems with the debate over the “national debt” is that there’s no generally agreed upon definition of that term. Is it what the federal government owes, or what it owes foreigners, or what the whole country, private and public sector together, owes? Does it include off-balance-sheet items and contingent liabilities?
There’s a hundred-trillion dollar gap between lowest and highest on this spectrum, which allows each commentator to confuse the rest of us by picking the measure that best suits their point of view. New York Times columnist Paul Krugman, for instance, uses “net debt” — the amount that the US owes foreigners — to argue that since this number is relatively small and slow-growing, we’re actually fine. Analysts using broader definitions of debt come to the opposite, more apocalyptic conclusion. Consider this from today’s Wall Street Journal, on the impact of off-balance-sheet obligations:
Smoke, Mirrors and Public Deficits
By RICHARD BARLEY
Are public debt and deficit numbers illusory? Perhaps, judging by the ruses employed by governments and identified by the International Monetary Fund’s Timothy Irwin in a recent staff note. Deficit crises in developed countries may only increase the allure of such devices, although they may do little to help in the long run.
European countries got creative as they strove to hit targets to join the single currency during the 1990s. In 2005, Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development researchers cataloged 192 cases of one-time measures and accounting maneuvers across Europe—50 in Greece alone—with effects ranging from negligible to 2% of GDP. In 1997, for instance, France took on the pension liabilities of France Télécom in exchange for a payment of €5.7 billion ($7.6 billion), or 0.5% of GDP.
But Europe wasn’t alone in playing games. In 2003, the U.S. proposed buying 100 refueling planes via operating leases, which would have kept the cost from being recognized upfront. The Congressional Budget Office said that was federal borrowing in disguise and would prove more expensive than a normal purchase.
The euro-zone debt crisis has put these techniques front and center. Portugal hit its 2011 target only via a transfer of bank pension assets that shaved 3.5 percentage points off its deficit.
Likewise, the U.K. is taking on the Royal Mail’s pension plan to pave the way for privatization. The plan brings with it £28 billion ($44.8 billion) of assets, thereby reducing the country’s 2012-13 deficit. But the U.K. is also taking on long-term liabilities on behalf of the company with a present value of £37.5 billion—which aren’t recognized immediately. So accounting transforms the Royal Mail’s pension deficit into a short-term gain for the U.K. budget but at a long-term cost.
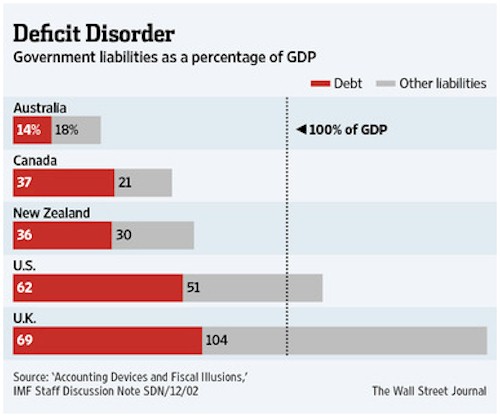
Keeping long-term liabilities out of the picture is a common tactic: In the U.S., debt was 62% of GDP in 2010, but including civil-service pension and other liabilities raises the total to 113%, Mr. Irwin notes. Public-private plans for infrastructure have also shifted upfront investment costs off-budget but have raised long-term debt risks—often through government guarantees.
The crisis has narrowed governments’ options. One way to flatter the statistics is via optimistic growth assumptions, although skeptical markets and the rise of independent fiscal watchdogs such as the U.K. Office for Budget Responsibility make this difficult. Another way is to shift cash flows forward, as Germany, Greece, Portugal and Belgium did in the past via securitizations of future government revenue. This, too, may now prove a tricky sell.
Investors trying to keep track of governments should remember Goodhart’s law: As soon as an indicator becomes a target for conducting policy, it loses its informational value. It also becomes a target for manipulation. That is a sobering thought given the euro zone’s obsession with deficit targets. They might just conceal problems building up elsewhere.
Then there are the “unfunded liabilities” of entitlements like Social Security and Medicare, which dwarf the official national debt. From a recent Zero Hedge article:
Massive $17 Trillion Hole Found In Obamacare
Two years ago, when introducing then promptly enacting Obamacare, the president stated that healthcare law reform would not cost a penny over $1 trillion ($900 billion to be precise), and that it would not add ‘one dime’ to the debt. It appears that this estimate may have been slightly optimistic… by a factor of 1700%. Because coincident with the recent Supreme Court debacle, in which a constitutional law president may be about to find that his magnum opus law is, in fact, unconstitutional, someone actually read the whole thing cover to cover, instead of merely relying on the CBO’s, pardon Morgan Stanley and Goldman Sachs’, funding estimates. That someone is Republican Jeff Sessions who after actually running the numbers has uncovered that the true long-term funding gap is a mind-boggling $17 trillion, just a tad more than the original sub $1 trillion forecast.
This latest revelation means that total underfunded US welfare liabilities: Medicare, Medicaid and social security now amount to $99 trillion! Add to this total US debt which in 2 months will be $16 trillion, and one can see why Japan, which is about to breach 1 quadrillion in total debt (yen, but who’s counting), may want to start looking in the rearview mirror for up and comer competitors. And while Obama may have been taking creative license with a number that is greater than total US GDP, he was most certainly correct when saying that Obamacare would not add a penny to US debt. Because the second the US government comes to market to fund a true total debt/GDP ratio of 750%, it is game over, and the Fed will have its hands full selling Treasury puts every waking nanosecond to have any time left for the daily 3pm stock market ramp.
Here’s a chart (compiled by John Williams’ Shadowstats) illustrating the impact of adding unfunded liabilities to the national debt:
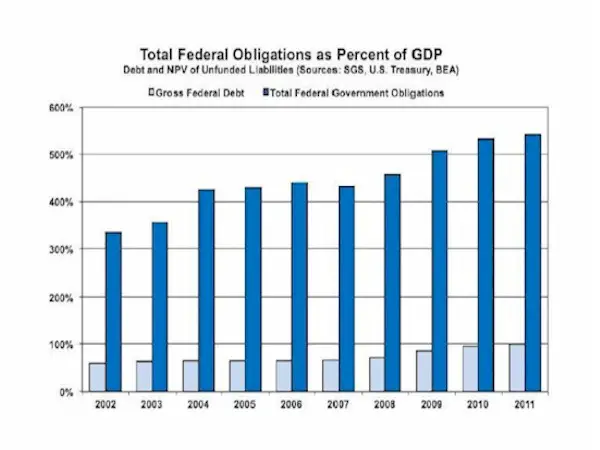
There are two reasons that debt and unfunded liabilities are treated as separate things:
1) The practice allows government to hide its true obligations in the same way that Enron did — right up to the day it evaporated. In other words, it’s a legally sanctioned lie.
2) Debt and unfunded liabilities are, at first glance, different in some ways. Debt is a legal obligation that gives the lender recourse, i.e. some way of getting back some of their money. In the private sector a lender who’s not getting paid can seize the borrower’s assets or force the latter into bankruptcy court where a judge decides who gets what. With sovereign debt, the creditor (who lent money by buying bonds) can sell those bonds and use the proceeds to buy up the borrower’s assets.
Unfunded liabilities, in contrast, are simply promises that don’t carry a legal obligation. In theory, Medicare could be cancelled tomorrow by Congress. Just like that, the program and its associated unfunded liabilities would disappear.
So the question becomes, how real — and therefore how dangerous — are US unfunded liabilities? The answer is that because they represent a promise to tens of millions of retired baby boomers who expect to get free money and health care for the last 30 or so years of life, they’re effectively more real an obligation than a Treasury bond.
A politician who messes with the Most Selfish Generation’s free health care will find himself back in the private sector before the polls close in the next election. Compare this with the probable repercussions of stiffing China or Saudi Arabia on bond interest — some contentious headlines and a bit of turmoil in the foreign exchange markets that most voters would hardly notice — and it’s clear that unfunded liabilities have, if anything, a more solid claim on future economic activity in the US than does interest on Treasury bonds.
So our true national debt is government debt plus private sector debt plus off-balance-sheet obligations plus unfunded liabilities, which comes to somewhere around half a million dollars per man, woman and child, or two million per family of four.
We can’t pay this of course, so the story of the next few years will be the search for the least painful way of breaking our promises. And history is pretty clear on this: a country with a printing press will always use it before exploring the harder options of actual default, whether through non-payment of interest or cancellation of benefits.
Dollar Collapse
No comments:
Post a Comment